Software projects are a complex and multifaceted process for both individual developers and teams. A successful project requires good planning, effective management and constant monitoring.
Identification of Needs: "What Will We Do?"
Questions that must be asked first to create the cornerstones of the project:
What is its purpose? For example, do you want to develop an e-commerce platform or a mobile game?
Who is the target audience? You should do research to understand your users' needs.
What's the problem? Clarify the problem you want to solve.
Real Life Example: A startup wanted to develop software that would make inventory management easier for small businesses. In the first step, they interviewed the businesses and identified the biggest challenges they faced.
Project Planning: "How Will We Do It?"
A successful project requires a clear roadmap. In the planning phase:
- Identify resources: Team members, budget, software tools.
- Create a timeline: Which phase will take how long?
- Risk analysis do: Anticipate possible problems and develop a plan B.
Real Life Example: An application development team divided a project that was supposed to be delivered within a two-month period into weekly sprints. Each sprint focused on completing a specific feature.
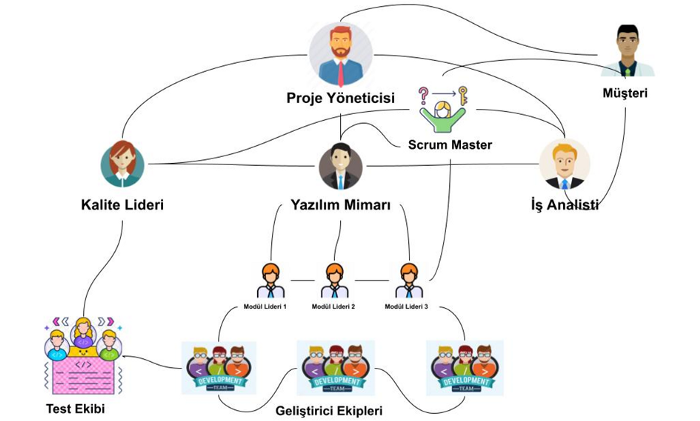
Design Phase: "What Will the User Experience Be Like?"
Design of the project should be user-friendly, both visually and functionally.
- Wireframing and prototyping: Create a rough draft of interfaces.
- User experience (UX) testing: Submit your designs to users' feedback
Real Life Example: In a mobile app development project, the team created a prototype using Figma and tested it with target users. This process enabled critical changes to the initial design of the application.
Development Process: "Coding and Technical Implementation"
After the design is approved, the coding process begins. At this stage:
- Determine a method such as Agile or Waterfall: Choose a project management methodology suitable for your team and your project.
- Create a coding structure: Clean and organized coding for a sustainable software Adopt standards.
- Use version control systems: Streamline the coding process with tools like Git.
Real Life Example: While a team is developing a customer management software, every two weeks Developed the software in delivered sprints. During this process, they managed the code by collaborating on GitHub.
Testing and Fixes: "Is Everything Working?"
The testing process is critical to verify the functionality and stability of the software.
- Perform unit and integration tests: Verify that each component of the software works individually and together.
- User acceptance tests (UAT): With real users have the software tested.
Real Life Example: A fintech app released its beta version to 100 users. Security and performance improvements were made based on feedback from users.

Launch and Distribution: "Time to Release to the World"
Your Software When it is ready, it is time to deliver it to users.
- Create a go-live plan: Release the project without errors.
- Determine marketing strategies: Social media, email to promote your product methods such as marketing or advertising campaigns
Real Life Example: A startup promoted its SaaS-based software with social media campaigns during launch and gained 500 new users in the first week.
Maintenance and Development: "Software is Never Finished"
The maintenance and development process continues after the software is published.
- User feedback Collect notifications: Consider users' suggestions and complaints
- Make regular updates: Keep software up to date with security patches and new features.
Real Life Example: A shopping app analyzes user feedback to create a “shipping tracking " feature and increased user satisfaction.
Success stories come to life with correct planning and effective management. You can achieve a successful result by following these steps before starting a project.




